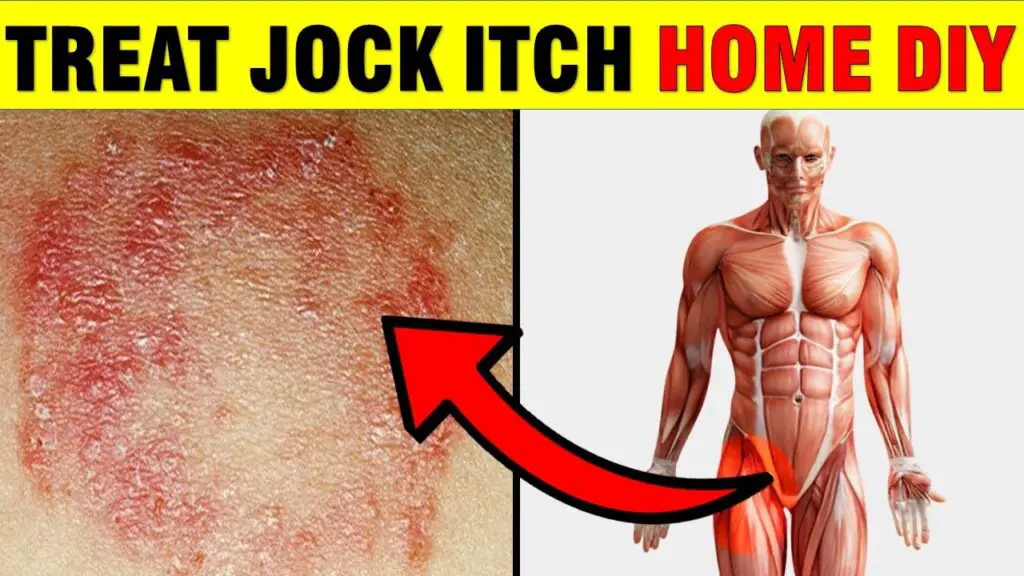
What Is Jock Itch?
Tinea cruris, commonly known as jock itch, is a fungal infection that typically develops in the skin folds around the groin, upper thighs, and buttocks.
Jock itch belongs to a group of fungal infections that affect the skin, called tinea. Athlete's foot is a well-known example of a fungal infection in this group, known as tinea pedis. Jock itch can be less severe than other tinea infections, but it can be irritating and painful nonetheless.
In tinea infections, symptoms are caused by mold-like, microscopic fungi known as dermatophytes. These fungi live on hair, skin, and nails. The fungi are often harmless, but they can cause infection allowed to multiply in moist, warm areas. This explains why jock itch typically occurs in skin folds.
A jock itch infection causes an itchy rash and other symptoms such as flaky skin or a burning sensation. Men, particularly during adolescence, typically have a higher chance of developing jock itch than women.
What Are The Symptoms Of Jock Itch?
The most common jock itch symptoms are as follows:
- Redness
- An itching or burning sensation
- A rash that worsens with physical activity or after using OTC hydrocortisone
- Changes in skin color
- Cracking, peeling, or flaky skin
- Unusual odor
These symptoms typically occur around the groin and inner thighs. The symptoms can spread to the buttocks and lower abdomen but won't usually affect the genital area.
Jock itch tends to start with intermittent itching, which gradually worsens. A rash will then appear, which may become dry and bumpy and even develop blisters. In women, the infection may present different symptoms such as white vaginal discharge and yeast infections.
A type of rash called ringworm can occur with fungal infections. Ringworm is named because of the red edge that surrounds the affected area.
The symptoms of jock itch typically come and go, and some cases of jock itch can resolve by themselves without any need for treatment. In most cases, however, jock itch will require treatment. Treatment usually involves applying topical antifungal medications and keeping the area clean and dry.
How Is Jock Itch Diagnosed?
In most instances, your doctor can diagnose jock itch simply by physically examining the affected area. The diagnosis will be based on your symptoms and the appearance of the affected area.
Occasionally, a healthcare professional may need to take a scraping of skin cells to be tested to diagnose the condition accurately. Testing the skin cells will rule out other skin conditions, such as eczema or psoriasis.How Is Jock Itch Treated?

You can usually relieve jock itch by keeping the affected area clean and dry and applying antifungal creams.
As well as applying topical antifungal treatments, people suffering from jock itch should wear clean clothes and underwear every day.
Because jock itch can be caused by wearing tight clothes or workout clothes that have gotten sweaty or dirty, make sure you wash workout clothes regularly and wear loose-fitting clothes while you wait for your symptoms to improve.
If you apply topical antifungal cream and maintain good hygiene but the jock itch symptoms persist, your health practitioner may prescribe stronger medicine.
A stronger prescription may include topical medications such as econazole or oxiconazole. Your doctor may also prescribe oral medications such as itraconazole or fluconazole.
Some oral antifungal medications can cause unpleasant side effects, including an upset stomach and headaches. If any side effects occur, get in touch with your doctor as soon as possible.
If your symptoms persist after two weeks of using home remedies, you should contact your doctor for further advice.
How Is Jock Itch Caused?
Jock itch is caused by an overgrowth of a group of fungi called dermatophytes. Because dermatophytes thrive in moist areas, jock itch is often caused by staying in sweaty clothes after exercising.
Jock itch is either caused by catching the fungal infection by coming into close contact with an infected person or excessive moisture occurring between skin folds and allowing the fungi to thrive. Some people are at higher risk of developing jock itch, but diet isn't a factor.
Is Jock Itch Contagious?
The fungus that causes jock itch is contagious. This means you can catch the fungal infection by being in close contact with a person who has jock itch, handling their unwashed clothing, or sharing towels with the infected person.
Are Some People At Higher Risk Of Jock Itch?
If the following factors apply to you, you may be at higher risk of developing jock itch:
- You're male
- You're an adolescent
- You're overweight or obese. This increases the number of skin folds you have, therefore allowing dermatophytes to thrive
- You have diabetes
- You tend to sweat profusely
- You are immunocompromised or take immunosuppressive medication
- You frequently wear tight-fitting clothes
- You have athlete's foot or another fungal infection
How Can I Prevent Jock Itch?
You can try the following practices to reduce your chances of developing jock itch.Good Hygiene

Regular hand washing and avoiding sharing towels with others will reduce your chances of getting jock itch from close contact with an infected person. Keep the skin around your groin clean and dry, washing the area as quickly as possible after exercising.
Ensure that workout clothes are removed and washed as soon as possible after your workout is complete, and other clothes and undergarments are washed regularly.
Wash The Area Regularly
You should keep the groin area clean by washing it frequently with soap and water. Washing the area is especially important after sweating because dermatophytes thrive in a moist environment.
Applying talcum powder to your groin area can help to soak up excess moisture.
Avoid Tight-Fitting Clothing
Wearing tight clothes and tight underwear increases your risk of developing jock itch because tight clothes can chafe your skin. Avoid tight-fitting clothes to reduce your chances of getting jock itch. Wearing boxer shorts rather than boxer briefs can help.
Seek Immediate Treatment If You Have Athlete's Foot
The same fungus that causes athlete's foot can spread and cause jock itch. The spreading of fungus can occur when putting on underwear or using the same towel to dry your feet and groin.
To avoid the infection spreading, get your athlete's foot treated as soon as possible and avoid using the same towel on your feet and your groin.
Is It Only Athletes Who Get Jock Itch?

The colloquial term for tinea cruris, jock itch, can imply that this infection only affects male athletes. However, jock itch can affect anyone. Those who exercise regularly can be at higher risk because of the increased chance of sweating between skin folds.
People who exercise regularly should prioritize washing their workout clothes and washing their groin area with soap and water as soon as possible after a workout.
What Are The Possible Complications Of Jock Itch?
Complications of jock itch are rare because jock itch is typically limited to the affected area and only affects the skin. Occasionally, the rash can spread from the groin to the genital area.
Severe cases of jock itch can develop symptoms such as open sores and ulcers. If you scratch the area excessively when it's itchy, secondary skin infections can occur and cause cellulitis or an abscess.
Another complication you may experience is post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation or hyperpigmentation. This is when the skin of the affected area becomes discolored as a result of the jock itch infection.
Why Is My Skin Still Discolored After The Infection Has Been Treated?
In some cases, skin discoloration in the groin area may continue for weeks after the fungal infection has been treated. This discoloration typically doesn't require treatment and should return to normal by itself eventually.
If you're concerned about continuing discoloration, your doctor will be able to provide medical advice and possibly prescribe something to help the discolored skin return to normal. This hyperpigmentation or hyperpigmentation rarely causes permanent scarring.
The Bottom Line
Jock itch is an irritating but minor fungal infection of the skin, usually affecting the groin area, upper thighs, and buttocks.
Jock itch can be easily avoided by practicing good hygiene and regularly washing clothes. People at higher risk of catching jock itch should pay extra attention to their hygiene practices and avoid wearing tight-fitting clothes.
To avoid developing jock itch, ensure that you wash your groin area and workout clothes immediately after exercising to prevent a build-up of excess moisture from occurring. The fungi that cause jock itch thrive in moist environments.
While symptoms can be irritating or even painful, jock itch luckily clears up within a couple of weeks with the help of antifungal creams and keeping the area dry and clean.
If you experience any of the symptoms of jock itch, get in touch with your health practitioner straight away for an accurate diagnosis.