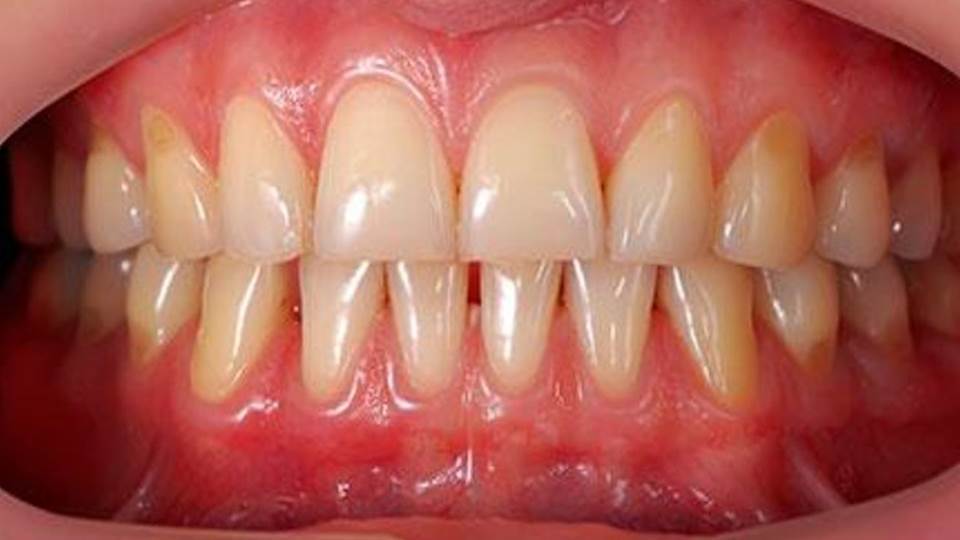
Gum recession is the clinical term for what happens when the gum tissue encompassing the tooth yanks back, revealing the root of the tooth. Receding gums can create visible gaps, allowing build-up of bacteria that stimulates disease.
If gum recession is not treated, the tooth’s bone structures and supporting tissue can be extremely damaged, which might lead to loss of teeth.
Due to its subtle onset, receding gums are an issue dentists are quite familiar with. Many people aren’t aware that they have gum recession since it happens progressively.
The initial symptom of gum recession tends to be a sensitive tooth. Also, one tooth might appear longer than other teeth around it. A slight notch or bump might be felt close to the gum line.
The initial symptom of receding gums might be a sensitive tooth and longer-looking teeth.
A dentist will seek out receding gum signs and suggest oral health hygiene steps to take, or recommend treatment to cease the recession.
According to the English NHS, many adults have a moderate amount of gum disease, which can result in gradual receding gums.
If you want to know more about receding gums then watch this video..........
The Negative impact of Receding Gums
Most individuals with receding gums aren’t worried about them at first. Others aren’t mindful that they’re going through the ordeal.
Some people might be worried about the following:
- Concerns about loss of teeth
- Fears about how they look
- Sensitivity because of tooth root exposure
Addressing worries about gum appearances starts with inspecting how much of the gums can be seen.
The gums are visible for some people when they smile and talk. For others, they might have a lip line that doesn’t reveal the gums at all.
Receding Gums: Why Does It Happen?
There are several reasons why gums might begin to recede, such as the following:
Rough brushing of teeth: Your tooth’s enamel might wear down if you brush too hard, which can result in receding gums.
Genetic predisposition: Genetics are the reason for most health issues, including dental health. Research indicates that over 30% of the population is at risk for gum disease due to their genetic DNA.
Hormonal changes: Transitions in levels of hormones during a female’s life, such as pregnancy, menopause, and puberty, could stimulate over-sensitivity of the gums, and eventually, gum recession.
Poor dental care: Inconsistent flossing, brushing, and rinsing allow bacteria to enter your mouth. Bacterial build-up results in tartar, a solid substance that can only be taken away during a tooth cleaning.
Periodontal diseases: Bone encompassing gum tissue can be destroyed by bacterial gum infections. Periodontal disease, aka gum disease, is the main cause of gum recession.
Natural gum recession: Gums might naturally shrink as time progresses in spite of proper oral hygiene steps taken. Though the term was made about horses, “long in the tooth” is suggestive of someone showing their age via recession of the gums.
- Grinding of teeth: Teeth grinding and clenching, usually done when someone is stressed out, can place more pressure on gums.
- Rough toothbrush: Gums can be damaged by overly firm bristles.
- Tobacco products and smoking: This bad habit hurts oral health as well as your lungs. Regular users have higher amounts of tooth plaque, which can result in recession.
- Uneven bite: Unaligned teeth can place extra pressure on gums, which results in recession.
- Oral piercing: Tongue or lip piercings can wear down and irritate gum tissue.
- Diabetes: Poorly managed diabetes impacts gum health.
Symptoms & Signs of Gum Recession
If you’re not careful, receding gums can hit you unexpectedly. Generally, recession of gums is a gradual process that you might not notice until roots of the teeth start to show. Gum recession is measured by your dentist in millimeters.
2 millimeters of attachment loss is considered important. Keep these signs in mind when determining if you have receding gums.
Sensitivity
Some of the roots are exposed to external elements when you have receded gums. They are not supposed to be exposed and usually react with hypersensitivity. Even brushing teeth along the gumlines can lead to extreme pain that feels as if you have nerve exposure.
Sensitivity is the result of the exposed root surfaces of the pores. Such pores contain nerve endings that reach outside the tooth from the inside.
During gum recession, stimulation can touch the pores and deliver alarming signals to the nerve.
Root Surface Exposure
Dentin is the part of the tooth that is beneath the enamel. Dentin looks yellow beside the white tooth enamel and can be seen when gums recede. Recession has transpired when you notice a yellow spot beside a defined white crown.
Swelling and Redness
You’ll endure some swelling and inflammation next to the gum recession area if it is associated with periodontitis or gum disease.
When tartar, plaque biofilm, and similar bacteria flourish under and close to the gumline, the body’s reaction is to take away the gums attached in that space. This results in receding gums and infection.
Longer Than Usual-Looking Teeth
During gum recession, the tooth’s root is exposed between the gumlines and the dental crown. The outcome is the look of a long tooth.
Just one of them might look long, or your whole smile might look like it’s full of long teeth. This look is the result of receded gums.
Gaps Between Teeth
The look of dark gaps between teeth close to the gumlines is the result of missing gum “papilla” between the teeth. During gum recession, this acute point of gum tissue is missing. It has crept away with other gum tissue supported.
The outcome is dark gaps between teeth that used to be covered with gum tissue.
Packing Food
During recession of the gums, gaps between teeth are created, allowing food to get lodged and packed in those spaces. Generally, you’ll notice at least one specific spot that food gets jammed in for the most part.
These spaces should be covered by gums naturally and stop food from lodging in those gaps. When food gets caught in problem spots, it starts to compound and stimulate a regular irritation and infection area when not properly taken away. This results in more gum recession.
Connection with Gum Disease
Food packed in gum pockets and between the teeth are formed close to the gumlines touching the teeth.
While gums recede, it also results in reduced tissue connected to the tooth’s root. Naturally healthy pockets in gums go as deep as 2 to 3 mm. Pockets get deeper when gums lose connectivity and become diseased.
If your receding gums measure 5 or 6 mm, it can be quite serious since there will be an extra 2 to 3 mm of unconnected gums inside the pocket (whether an infection is apparent or not).
If infection is apparent, the pocket can be at least 4 mm. Receding gums can be a cause for concern and be indicative of tooth loss down the road when mixed with deep gum disease pockets.
What is the Best Treatment for Minor Gum Recession?
Recovery of gums can transpire from moderate gum recession with the assistance of a detailed cleansing form a dentist. This might be comprised of manual or ultrasonic tooth scaling to take away tartar and plaque and prevent it from accumulating again.
Antibiotics might be necessary if gums become infected.
Gum surgery might be required if conservative treatment proves to be ineffective. This might warrant a visit to a periodontist dental surgeon specialist.
HERE ARE 10 METHODS OF TREATING RECEDING GUMS NATURALLY
Let’s talk about some simple and natural approaches to dealing with receding gums:
1. SESAME SEED OIL RINSE
Sometimes referred to as ‘oil pulling’ in Ayurvedic medicine, you’ll undergo some terrific benefits with a sesame seed oil rinse. Sesame oil contains strong antibacterial and anti-inflammatory compounds.
For approximately 15 minutes, swish a tablespoon of sesame oil (or until the oil gets thinner). Rise your mouth with fresh water after you spit the liquid out. Do this every day for 30 days straight.
One of the simplest ways to ease pain, inflammation, and gum recession is to rise your mouth with salt and warm water.
Dissolve a moderate amount of sea salt into a cup of warm water before swishing the concoction in your mouth for approximately 15 seconds, then spit it out. For optimal outcomes, do this up to three times daily.
Coconut oil is an impactful gum disease treatment. When combined with baking soda, coconut oil purges your mouth of acids that cause bacteria.
Combine a couple of tablespoons of baking soda and coconut oil. This concoction will act as a toothpaste replacement a couple of times a week until the issue resolves.
4. CHAMOMILE TEA
There are potent antiseptic compounds in chamomile flowers. They aid in minimizing inflammation that comes with gum recession and disease.
Add up to three tablespoons of chamomile tea into a cup of hot water. Let the concoction steep for approximately 10 minutes before you strain and cool it. This process should be repeated a few times daily for as long as it takes.
5. MYRRH MIX
For sore gum treatment, myrrh is an effective solution. 10 to 12 drops of myrrh tincture should be added to a warm cup of water. This concoction will act as a mouthwash as part of your regular oral health routine.
6. TEA TREE OIL
Much like other ingredients in this article, tea tree oil has some amazing anti-inflammatory and antibiotic compounds. A 2008 Australian study found that ongoing application of tea tree oil minimizes gingivitis and gum bleeding.
Add up to a couple of drops of tea tree oil onto your toothbrush, or combine it with your toothpaste. That is all that’s required! Keep brushing using this essential oil a couple of times daily for three weeks.
7. SEPTILIN
The Ayurvedic medicine, Spetilin, has been proven to enhance immunity. This conventional medicine is a combination of elements that, besides assisting a healthy immune system, also minimizes inflammation.
Based on a study released by the Journal of Periodontal Implant Science, Spetilin – when used as a dietary supplementation - enhances periodontal treatment results in only a few weeks. If you want to purchase Septilin Click Here
8. FLOSSING
Flossing with a natural compound aids in minimizing plaque and bacteria just as effectively as oil pulling.
Best of all, you don’t have to floss every day. Flossing twice a week, in addition to maintaining a proper oral hygiene regimen, might be sufficient in stopping gums from receding.
9. CRANBERRY JUICE
Cranberry juice is very concentrated with vitamin C and acts as an amazing antioxidant that can treat oral health issues. Cranberry juice has proven to be impactful in warding off oral infections and receding gums. Studies show that minimal vitamin C intake is associated with a greater risk of periodontal disease.
Consuming four ounces of cranberry juice daily might aid bacteria from gathering and solidifying in the teeth. Other potent sources of vitamin C are grapefruits, oranges, papaya, strawberries, red pepper, and broccoli.
10. GREEN TEA
Renowned for its anti-aging composites, green tea was discovered by Japanese scientists, and aids in promoting healthy gums and teeth.
A study found in the Journal of Periodontology revealed that consuming one cup of green tea daily lowered periodontal pocket depth, enhanced the connection of the teeth to the gums, and minimized gum bleeding.
The results were bolstered with more cups of green tea consumed. Much like cranberry juice, green tea optimizes healthy gums.
CONCLUSIONS
I hope this article has been helpful in showing you what are the causes of gum recession and the natural ways you can treat Gum Recession at Home.

If you would like to know what I consider the best product to treat gum recession and best of all its not that expensive and its natural then CLICK HERE
The product I would recommend is Gum Recession rescue tooth powder.
It helps provide support for moderate or serious teeth, gums and mouth issues. It works great to eliminate gum problems and helps to reverse gum recession and gum inflammation. It can also soothe bleeding gums, tighten loose teeth and remove plaque build-up.